At Sainik School Amaravathi Nagar, Thamizh Nadu, we had an MI Room (Medical Inspection Room) – the refuge for the tired souls – both physical and mental. The boss out there was Mr KP Damodaran who can well be described as a Nursing Assistant by profession, whom everyone called a Compounder, but always acted as a Doctor.
Forever for any medical condition, worth it or not, he prescribed a combination of APC with sodium-bicarbonate, a pink coloured magic potion, an awful tasting mixture, compounded by our Compounder Mr Damodaran, a Veteran from the Royal Indian Navy who saw action during World War II.
I was admitted for mumps in the isolation ward for 21 days while in grade 7. During one of his daily rounds, Mr Damodaran saw me reading the history book. As he turned the pages, it was about the Viceroys and Governor Generals of British India – Lord Wavell and Mountbatten. Mr Damodaran said “I’ve met both Lord Wavell and Lord Mountbatten during World War II. Lord Wavell’s sketch in this book least resembles his personality.”
What was the magic tablet APC? It was a combination tablet containing aspirin, phenacetin and caffeine. In those days (early 70’s), it was perceived to be a magic drug – a solution for most diseases and medical conditions. It disappeared in 1983 because of harmful side effects of phenacetin.
Sodium-bicarbonate is a mixture of Sodium-bicarbonate with sugar and salt. It was used as an antacid to treat heartburn, indigestion and upset stomach as Sodium-bicarbonate is a very quick-acting antacid.
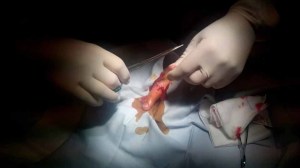
When we were in grade 11 in 1978, we were the senior-most in school. During a movie show on a Saturday night, a bench we were seated broke and a piece cut through the thigh of Palanivel, our classmate. Everyone else were engrossed in watching the movie, but I saw Palani bleeding and writhing in pain. I helped him walk to the MI Room and there was Mr Damodaran.
Palani was immediately administered a dose of Tetanus Toxoid (TT) and the next step was to suture his six inch long gash. Mr Damodaran switched on the steriliser and after five minutes asked me “put on the gloves and take out the suturing thread and a needle with a tong.” I did as ordered.
Then came a surprise ordeal for me. Mr Damodaran had a failing eyesight and he asked me “Please thread the needle.” Unfortunately for us, Mr Damodaran’s spectacles broke a few days before and to get a new one he had to travel to Udumalpet, the closest town, about 24 km away. That could be feasible only the next day being a Sunday.
His next command was a bigger surprise – “now start stitching.” He instructed each step and I put six sutures through Palani’s skin. Palani must still be carrying the scar on his thigh today.
How could I execute such a mission?
When we were in Grade 2 & 3, we had stitching classes by Annamma Teacher, who also taught us Malayalam. On a piece of cloth we began with hemming, then running stitch, cross stitch and then stitch English Alphabets, a flower and a leaf. It came in handy that day.
Annamma Teacher remains etched in my memory as she was very compassionate to the young kids and was an epitome of dedication. She was always dressed in her spotlessly white ‘Chatta, Mundu and Kavani,‘ the traditional Syrian Christian women’s attire. Chatta is more like a jacket, while the mundu (dhoti), unlike the one worn by a man, is elegance personified, especially at the back, where it is neatly pleated and folded into a fan-like ‘njori‘. Both Chatta and Mundu are pure cotton, Kavani, generally off-white with hand sewn embroidery is made of a thinner material and is draped across the body.
During our younger days, Chatta, Mundu and Kavani was the most common wear for the ladies, especially while attending the Sunday Mass and also during social and religious occasions. Chatta consists of two pieces of cloth cut into T shape and hand stitched prior to the arrival of sewing machines. My grandmother said that they used to cut the cloth into two Ts with a kitchen knife as the scissors were not in vogue then and hand sew them.
Muslim women of Kerala in those days wore a white Mundu called ‘Kachimundu’ with blue and purple borders. The Muslim women’s Mundu do not have the fan-like Njori at the back. The head covering ‘Thattam‘ is better known as ‘Patturumala.’ The torso is covered by a long blouse with full sleeves. This type of dress is known as Kachi and Thattam.
Difficulty in maintaining the white outfit spotlessly white and availability of cheaper, easy to wear and maintain sarees resulted in the saree becoming the common wear for the Syrian Christian ladies. Modern day wedding planners have revived the Chatta, Mundu and Kavani by showcasing it by asking a few relatives of their client to dress up so.
Annamma Teacher’s son, Veteran Colonel OM Kuriakose and her grandson Lieutenant Colonel Anish Kuriakose – both father and son are from The Parachute Regiment of the Indian Army.